-
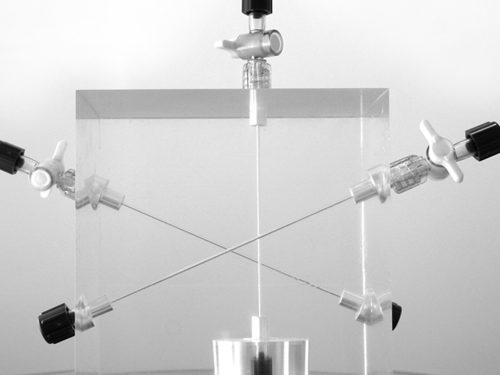
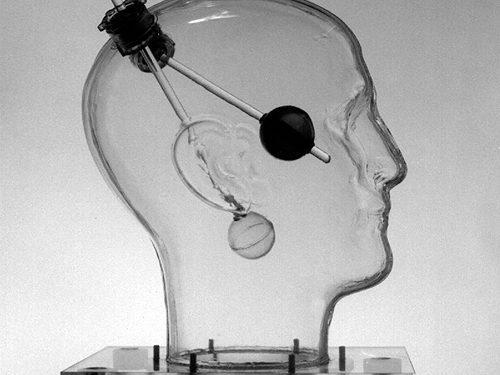
 An integrated MR QA system for MR guided surgery and radiotherapy MRI manufacturers have made great strides in reducing MR system distortion. Maintaining acceptable levels of distortion relies on properly controlling a long chain of conditions. It is critical to have a robust system of quality control for key imaging performance characteristics in order to detect significant deviations before they affect clinical operations.
An integrated MR QA system for MR guided surgery and radiotherapy MRI manufacturers have made great strides in reducing MR system distortion. Maintaining acceptable levels of distortion relies on properly controlling a long chain of conditions. It is critical to have a robust system of quality control for key imaging performance characteristics in order to detect significant deviations before they affect clinical operations. -
 Large MRI phantom for comprehensive evaluation of critical imaging parameters of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a time efficient manner. The phantom can be used for the measurement of absolute values for calibration purposes. However, its design is optimized for time efficient daily quality assurance too.
Large MRI phantom for comprehensive evaluation of critical imaging parameters of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a time efficient manner. The phantom can be used for the measurement of absolute values for calibration purposes. However, its design is optimized for time efficient daily quality assurance too. -
 ACR accredited Medium MRI phantom for comprehensive evaluation of critical imaging parameters of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a time efficient manner. The phantom can be used for the measurement of absolute values for calibration purposes. However, its design is optimized for time efficient daily quality assurance too.
ACR accredited Medium MRI phantom for comprehensive evaluation of critical imaging parameters of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a time efficient manner. The phantom can be used for the measurement of absolute values for calibration purposes. However, its design is optimized for time efficient daily quality assurance too. -
 This phantom can be used to check the alignment of the internal and external lasers to the radiographic centre of CT and PET/CT units and to verify lateral gantry angle. It can also be used with accelerator units to check vertical and lateral gantry angles, laser alignment and vertical table movement.
This phantom can be used to check the alignment of the internal and external lasers to the radiographic centre of CT and PET/CT units and to verify lateral gantry angle. It can also be used with accelerator units to check vertical and lateral gantry angles, laser alignment and vertical table movement. -
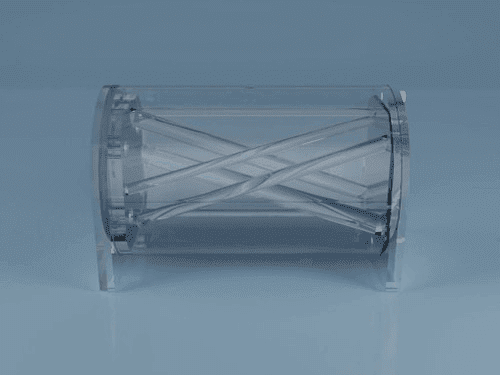 The Phantom designed for a simple and cost effective verification of image alignment and distortion in hybrid scanning systems like PET/CT or NM/CT. It consists of a cylinder that can be filled with a variety of fluids. Several non-parallel rods of varying diameter and at certain angles in relation to the phantom’s axes run the entire length of the cylinder.
The Phantom designed for a simple and cost effective verification of image alignment and distortion in hybrid scanning systems like PET/CT or NM/CT. It consists of a cylinder that can be filled with a variety of fluids. Several non-parallel rods of varying diameter and at certain angles in relation to the phantom’s axes run the entire length of the cylinder. -
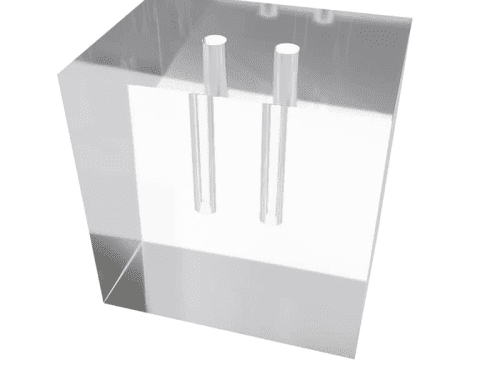 This scatter phantom simulates in-vivo forward and backscatter characteristics of 99mTc gamma rays for the extrinsic measurement of a scintillation camera’s deadtime. The phantom produces a spectrum typical of that observed from 99mTc in the myocardium. Reference: Ralph Adams, Gerald J. Hine, and C. Duane Zimmerman, “Deadtime Measurements in Scintillation Cameras Under Scatter Conditions Simulating Quantitative Nuclear Cardiography,” The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 19 (1978), 538-544.
This scatter phantom simulates in-vivo forward and backscatter characteristics of 99mTc gamma rays for the extrinsic measurement of a scintillation camera’s deadtime. The phantom produces a spectrum typical of that observed from 99mTc in the myocardium. Reference: Ralph Adams, Gerald J. Hine, and C. Duane Zimmerman, “Deadtime Measurements in Scintillation Cameras Under Scatter Conditions Simulating Quantitative Nuclear Cardiography,” The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 19 (1978), 538-544. -
 A simple phantom the quality assurance of geometric distortion and spatial resolution of gamma cameras. Array of holes, which when filled with activity, allows to measure point-to-point distances and Point Spread Function (PSF) - spatial resolution - at each point and its homogeneity across the entire Field of View.
A simple phantom the quality assurance of geometric distortion and spatial resolution of gamma cameras. Array of holes, which when filled with activity, allows to measure point-to-point distances and Point Spread Function (PSF) - spatial resolution - at each point and its homogeneity across the entire Field of View.